Right Angle Triangle
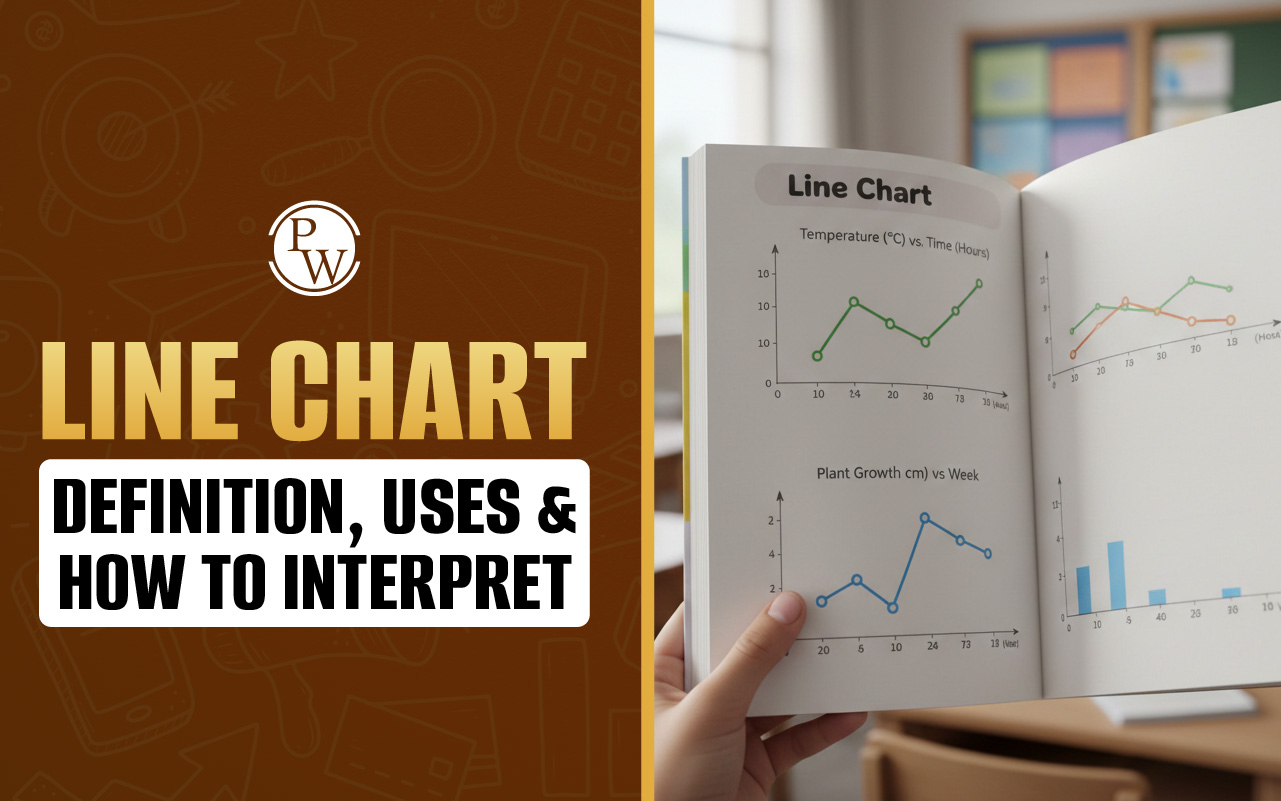
A right angle triangle is one of the most fundamental shapes in geometry. Many students often ask, "what is right angle triangle?" A Right angled triangle is a special type of triangle with one angle measuring exactly 90 degrees. The side opposite the right angle is the longest side, which is called the hypotenuse. The other two sides, which form the right angle, are known as the base and the perpendicular (or height).
When exploring types of right angle triangle, you can find isosceles and scalene variations. To clarify, "what is right triangle" simply refers to the same concept as a right angle triangle. Right-angled triangles have unique characteristics that make them distinct.
For example, in ΔABC, if angle ∠ABC = 90°, then ΔABC is a right-angle triangle. Side AB is the perpendicular, and side BC is the base. The longest side, AC, is the hypotenuse.
Right Angle Triangle Definition
A right angle triangle definition states that it is a triangle with one angle measuring exactly 90 degrees. Understanding right angle triangle formula is essential for solving problems involving sides and angles, such as the Pythagorean theorem.
The right angled triangle definition states that “if one of the angles of a triangle is 90°, the triangle is named as a right angled triangle or right triangle”.
Right-angled triangles are not just a part of geometry, they appear in everyday life too. For example, the triangular slice of bread, a square sheet of paper folded along its diagonal, the slanted roof of a house, or the 30°-60°-90° triangular scale in a geometry box are all real-life examples of right-angled triangles.
Read more: 30°- 60°- 90 triangle
Right Angle Triangle Properties
Let’s understand the main properties of a right angled triangle:
-
One angle of a right-angled triangle is always exactly 90 degrees.
-
The hypotenuse, opposite the right angle, is always the longest side.
-
The other two angles are always acute and together equal ninety degrees.
-
The sides of a right-angled triangle always follow the Pythagoras theorem.
-
A right-angled triangle cannot have any obtuse angle at all.
-
Trigonometric ratios such as sine and cosine are based on the sides of a right-angled triangle.
Read more: Tricks to remember trigonometric values
Right Triangle Formula
By using the right angle triangle formula and observing right triangle examples, students gain a clear understanding of the types of right angle triangle and their properties. After understanding the concept of what is a right triangle, let’s now learn the right triangle formula. According to the Pythagoras Theorem, in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse, which is the side opposite the right angle, is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, the base and the perpendicular or height.
The right triangle formula is expressed as:
Hypotenuse2 = Base2 + Perpendicular2
Read more: Perfect Square
Area of Right Angled Triangle
The area of a right angled triangle is the amount of flat space enclosed within the three sides of the triangle. The area of right angle triangle is expressed by the following formula:
Area of right angled triangle = ½ x Base x Height
It tells us how many square units can fit inside the right triangle.
Perimeter of a Right Angled Triangle
The perimeter of a right angled triangle is the total length of all its three sides. The perimeter of a right triangle is calculated using the following formula:
Perimeter of a right triangle = Base + Perpendicular + Hypotenuse
Right Angled Triangle Trigonometry Ratios
For a right triangle, the trigonometric functions for any angle θ are defined as follows:
sin θ = Opposite Side/Hypotenuse
cos θ = Adjacent Side/Hypotenuse
Types of Right Triangles
Right-angled triangles are classified into two types based on the nature of the other two angles or sides. The two types of right angle triangle are:
Isosceles Right Triangle
An isosceles right triangle is a right angled triangle in which the two sides that form the right angle are equal in length. Since these sides are equal, the two angles opposite them are also equal, and each measures 45°. Therefore, the three angles of this triangle are always 45°, 45°, and 90°.
Scalene Right Triangle
A scalene right triangle is a right angled triangle in which all three sides have different lengths. It has one angle that is exactly 90°, while the other two are acute angles but not equal to each other. This makes the scalene right triangle different from the isosceles type.
Read more: Scalene Triangle
Right Triangle Examples
Studying right triangle examples, like the classic 3-4-5 triangle, helps in applying theory to practice. After getting acquainted with the right-angle triangle definition and properties, students must go through some right triangle examples that apply the right triangle formula, as given below:
Example 1: A right-angled triangle has base 6 cm and height 8 cm. Find the hypotenuse.
Solution:
Using Pythagoras' theorem, we can write
Hypotenuse (h) = √ [(6)² + (8)²] = √ 36 + 64 = √ 100 = 10
So, the hypotenuse of the given triangle is 10 cm.
Example 2: A right triangle has height 5 cm and base 12 cm. Finds its area and perimeter.
Solution:
Base = 9 cm, Height = 12 cm,
So, Hypotenuse = √ [(5)² + (12)²] = √25 + 144 = √169 = 13 cm
Area = (1/2) × base × height
= (1/2) × 5 × 12 = 30 cm²
Perimeter = base + height + hypotenuse
= 5 + 12 + 13 = 30 cm
Example 3: A ladder is leaning against a wall. The base of the ladder is 3 m away from the wall, and the ladder touches the wall at a height of 4 m. What is the length of the ladder?
Solution:
The ladder acts as the hypotenuse, the wall is the perpendicular, and the ground is the base.
Here, base = 3 m and perpendicular = 4 m.
If the length of the ladder is taken as ‘l,’ then according to the hypotenuse formula, we can write:
(l)² = (3)² + (4)²
Or, (l)² = 9 + 16 = 25
Or, l = √25 = 5
So, the length of the ladder is 5 meters.
Read more: Pythagorean Triples
Right Angle Triangle Applications
The right angle triangle is not just an academic concept; it has useful applications in many branches of mathematics and science as well as in other fields, as mentioned below:
-
Construction and Architecture: Designing bridges, buildings, and roof structures often involves right triangle concepts.
-
Navigation and Surveying: Right triangle formulas help measure distances during navigation and surveying.
-
Physics: Diagrammatic representation of forces, motion, and vectors often involves right triangles.
-
Everyday Life: Positioning ladders, and climbing ramps or slopes, all relate to right triangle principles.
The right-angle triangle is a very important concept in mathematics. It forms the basis of many applications in physics, architecture, and real-life scenarios. Through the right-angle triangle definition, formula, and examples, students can gain a better understanding of this concept and its applications.
Make Maths Easy and Fun for Your Child with CuriousJr
Is your child struggling with maths, losing confidence, or finding lessons boring? CuriousJr Maths Online Classes help turn these challenges into learning opportunities. Our platform makes maths engaging, interactive, and stress-free. With CuriousJr, your child can:
-
Understand difficult concepts quickly through fun lessons and games
-
Improve problem-solving and critical thinking skills
-
Build speed and accuracy in calculations
-
Gain confidence and enjoy learning
Parents can track progress, celebrate milestones, and support their child’s growth every step of the way. With CuriousJr, maths becomes not just manageable but something your child looks forward to every day. Book a demo class today to know more about our classes.