Class 6 Social Science Chapter 3: Landforms and Life – NCERT Solutions
Class 6 Social Science Chapter 3 Landforms and Life, helps students understand how different landforms affect human activities and natural life. These NCERT solutions explain important topics like mountains, plateaus, plains, deserts, and coastal areas in an easy and clear manner. In this chapter, students learn how mountains influence climate and support activities such as tourism and farming on terraces. Plains are shown as fertile regions where most people live due to easy farming, transport, and trade. Plateaus are rich in minerals and support mining and industries. Deserts teach students about harsh living conditions and how people adapt to them, while coastal areas highlight fishing, ports, and trade.
Landforms are the natural physical features of the Earth's surface. class 6 social science chapter 3 questions answers help students comprehend why people live in different places around the world. The surface of the Earth is not the same everywhere; it has different features that were made by processes inside and outside the Earth. The internal processes cause the earth's surface to rise or fall, while the external processes cause the land to be worn down and rebuilt over and over again.
These solutions are useful for homework, exam preparation, and quick revision. By studying Landforms and Life Class 6 NCERT solutions, students develop a clear understanding of how landforms shape human life and the environment, building a strong foundation for future geography lessons.
Vishwas Diwas With PW: India's Biggest Education Festival Live from 28th Feb 2026
Class 6 Social Science Chapter 3 Landforms and Life Questions Answers
NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Social Science Chapter 3 Landforms and Life are provided below to help students understand the concepts thoroughly and prepare well for exams.
These solutions cover all important questions, activities, and exercises from the chapter. By going through these answers, students can strengthen their knowledge and practice according to the latest syllabus and exam pattern.
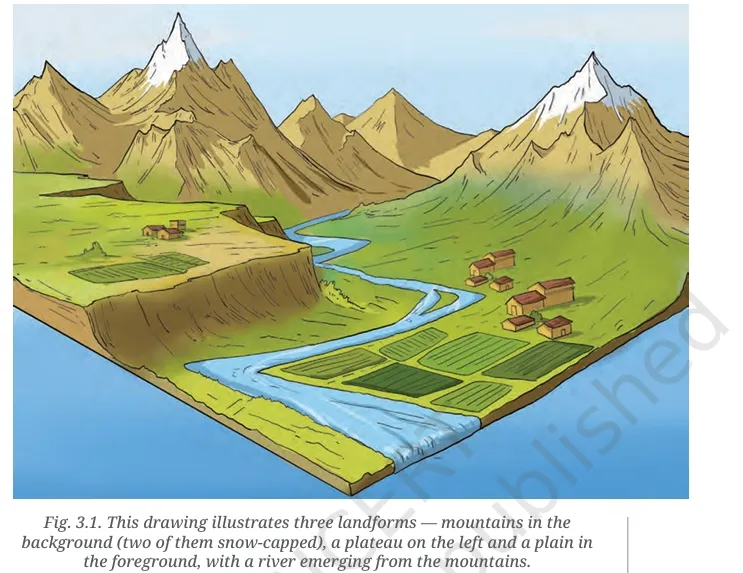
-
What are the major types of landforms and their significance to life and culture?
The major landforms are mountains, plateaus, and plains.
-
Mountains influence climate, provide water through rivers, support unique flora and fauna, and are often regarded as sacred.
-
Plateaus are elevated flatlands rich in minerals that support mining, and in some regions, agriculture.
-
Plains have fertile soil suitable for agriculture, support dense populations, and enable cultural and economic development.
-
What are the challenges and opportunities of life associated with each landform?
-
Mountains: Challenges include landslides, avalanches, harsh climate. Opportunities include tourism, terrace farming, and pilgrimages.
-
Plateaus: Challenges include less fertile soil. Opportunities include mining, waterfalls, and tourism.
-
Plains: Challenges include floods, overpopulation, and pollution. Opportunities include fertile agriculture, river navigation, and trade.
Let’s Explore Activities

-
Observe the school’s surroundings. What kind of landscape do you see? Will the landscape change within 50 kilometres?
Example: The school is in a plain area. The landscape will change to hilly regions within 50 km.
-
Discuss a journey through a region of India. List different landscapes seen on the way.
Example: Journey from Delhi to Nainital: flat plains, gentle hills, and steep mountains.
-
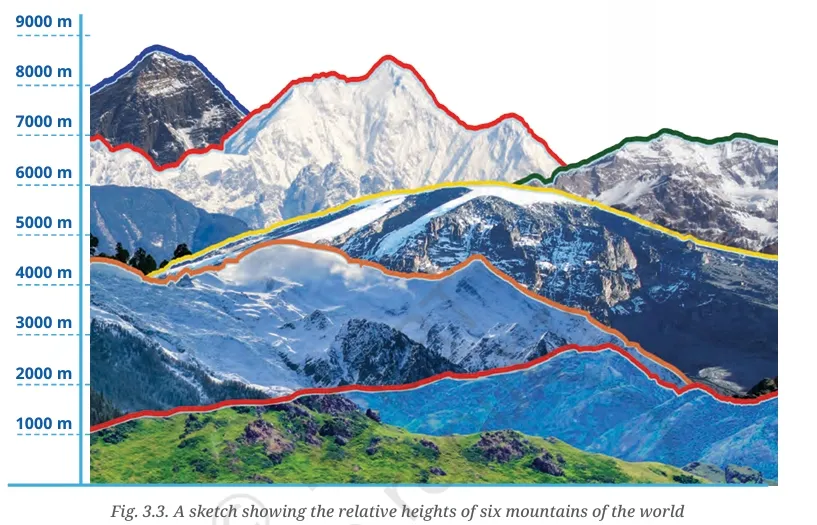
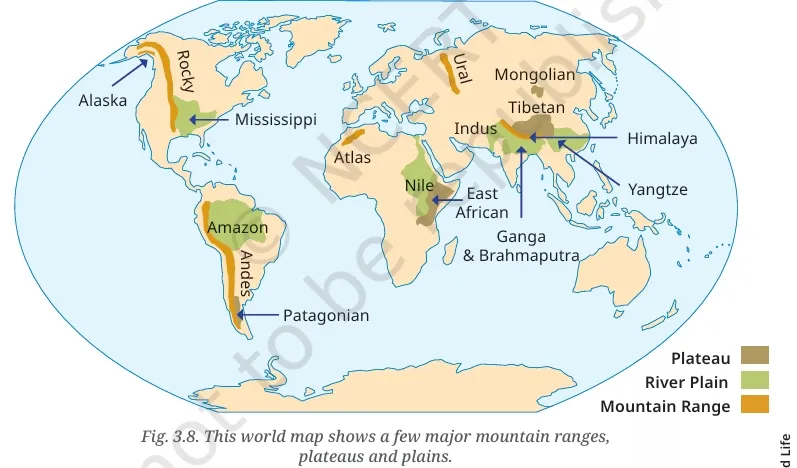
Which colour is the Ganga plain?
Green.
-
What does the white expanse represent?
Snow-covered Himalayas or high-altitude regions.
-
What does the brown expanse at the bottom left represent?
Hilly or mountainous areas.
-
Examples of sacred river sources or confluences from your region?
Examples: Prayagraj (confluence of Ganga, Yamuna, and Saraswati), Gangotri (source of Ganga).
-
Name some popular tourist destinations in India and identify their landforms.
Shimla – Mountain
Goa – Coastal plain
Jaipur – Plateau region
Varanasi – Plain
Chapter-end Questions
-
In what type of landform is your town/village/city located? Which features mentioned in this chapter do you see around you?
Example: My city is in the plain region. I see fertile fields, river systems, and agricultural settlements.
-
Describe the three landforms you came across on the way from Chhota Nagpur to Prayagraj and Almora.
Chhota Nagpur – Plateau with minerals and forests
Prayagraj – Plain with fertile soil and rivers
Almora – Mountainous region with steep slopes and forests
-
List a few famous pilgrimage spots in India along with the landforms in which they are found.
Kedarnath – Mountain
Varanasi – Plain
Amarnath – Mountain
Rameswaram – Coastal plain
-
State whether true or false
-
The Himalayas are young mountains with rounded tops. False
-
Plateaus usually rise sharply at least on one side. True
-
Mountains and hills belong to the same type of landform. True
-
Mountains, plateaus and rivers in India have the same types of flora and fauna. False
-
Ganga is a tributary to the Yamuna. False
-
Deserts have unique flora and fauna. True
-
Melting snow feeds rivers. True
-
Sediments from rivers deposited in the plains makes the land fertile. True
-
All deserts are hot. False
-
Match words in pairs
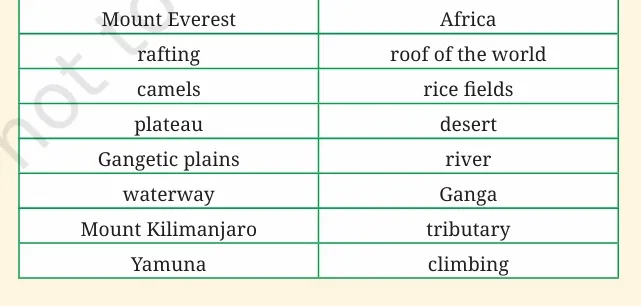
Mount Everest – climbing
rafting – waterway
camels – desert
plateau – roof of the world
Gangetic plains – rice fields
Mount Kilimanjaro – Africa
Yamuna – tributary
Ganga – river
Read More: Ecosystem
Detailed Study of Mountains, Plateaus, and Plains
According to the NCERT curriculum, landforms are broadly categorized into three types based on elevation and slope. These sections mirror the depth found in standard reference materials to help students prepare for their examinations effectively.
1. Mountains: The Giants of the Earth
A mountain is a natural elevation of the earth's surface that is considerably higher than the surrounding area. They often have a small summit and a broad base. In some mountains, there are permanently frozen rivers of ice known as glaciers.
Characteristics of Mountains:
-
Climate: The climate in mountain regions is often very harsh (cold), which is why fewer people live there.
-
Slopes: Because the slopes are steep, there is less land available for farming.
-
Range: When mountains are arranged in a line, they are referred to as a range (e.g., the Himalayas, the Alps, and the Andes).
Types of Mountains:
-
Fold Mountains: Created when tectonic plates collide (e.g., Himalayas).
-
Block Mountains: Formed when large areas are broken and displaced vertically. The uplifted blocks are called horsts and the lowered blocks are grabens.
-
Volcanic Mountains: Formed due to volcanic activity (e.g., Mt. Kilimanjaro).
2. Plateaus: The Elevated Tablelands
A plateau is an elevated flat land. It is a flat-topped tableland standing above the surrounding area. Plateaus can have one or more sides with steep slopes.
-
Importance: Plateaus are very useful because they are rich in mineral deposits. Many of the mining areas in the world are located in plateau regions.
-
Examples: The Deccan Plateau in India is one of the oldest. The Tibet Plateau is the highest in the world.
-
Scenic Beauty: Plateaus often have waterfalls, such as the Hundru Falls in the Chhota Nagpur plateau.
3. Plains: The Cradle of Civilizations
Plains are large stretches of flat land, generally not more than 200 metres above mean sea level. They are usually formed by rivers and their tributaries.
-
Fertility: The rivers carry forward eroded material and deposit stones, sand, and silt along their courses and in their valleys. This makes the land extremely fertile.
-
Human Habitation: Plains are the most useful areas for human habitation. It is much easier to build houses, roads, and carry out farming on flat land. Consequently, plains are the most thickly populated regions of the world.
Read More:
Make Social Science Easy with CuriousJr Online Tuition Classes
To further enhance your understanding of Geography and Social Sciences, CuriousJr offers online tuition courses for young learners from Classes 3 to 8. These courses focus on concept-based learning rather than rote memorization. Through interactive videos, real-life examples, and engaging activities, students can easily understand topics such as landform formation, climate, natural resources, and the relationship between landforms and human life.






